Beacon Machine Manufacturing Co.,ltd
Guide to Inspection and Adjustment of VE Distributor Fuel Injection Pump Systems
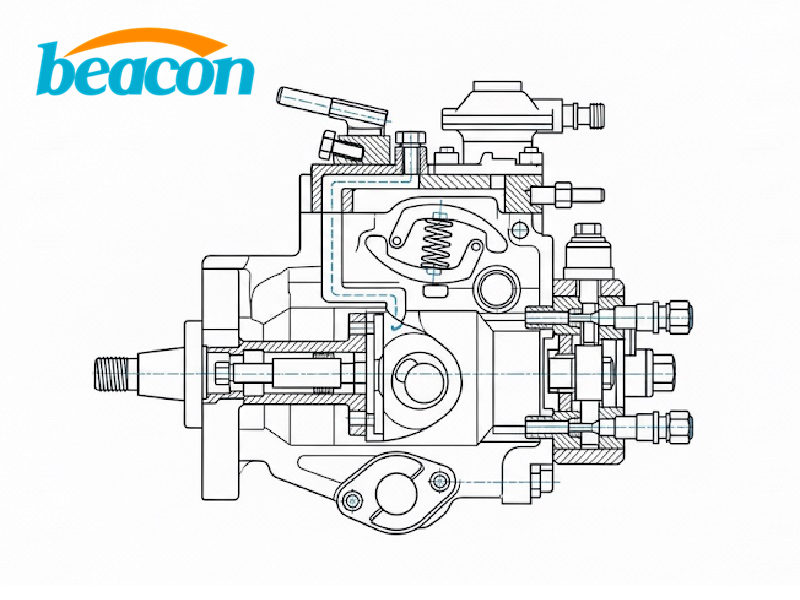
Inspection and Adjustment of VE Distributor Fuel System
The VE distributor pump differs significantly in structure from the mechanical inline injection pump, and its working principle is also different. Therefore, the on-vehicle removal and installation of the VE pump also differ significantly from the mechanical inline injection pump.
(1) Key Points for Disassembly and Assembly of VE Distributor Pump
① Locking the Injection Pump Shaft: To ensure the correct fuel supply timing of the injection pump, it is not necessary to readjust during assembly, reducing unnecessary work processes. The injection pump shaft should be locked when the diesel engine is at the compression top dead center (TDC) of the first cylinder.
The method is: Turn the diesel engine crankshaft to the compression TDC of cylinder 1, insert the process positioning pin, then loosen the injection pump shaft locking nut, remove the locking plate, and tighten the nut again with a torque of (13 ± 2) N·m. The injection pump shaft is now locked. Place the locking plate in a location where it is easy to retrieve and pull out the process positioning pin.
② Making Marks: After scribing a line on the gear chamber and the injection pump fixing bolt hole as a mark, the injection pump can be removed from the diesel engine.
③ Assembly Sequence and Techniques:
Step 1: Turn the drive shaft clockwise so that the process positioning pin inserts into the groove on the back of the convex gear (i.e., cylinder 1 plunger is at the compression TDC position).
Step 2: Install the injection pump seal gasket on the 3 stud bolts at the rear of the gear chamber and install the injection pump. Tighten the nuts by hand for 3 ~ 4 turns; the injection pump should be able to rotate freely on the bolts.
Step 3: Remove the locking nut and washer from the pump shaft, install the semicircular key (Woodruff key), ensuring the top surface of the key is parallel to the shaft axis; then install the drive gear, aligning the "C" point on the gear with the "0" point on the convex shaft gear.
Step 4: Use a torque of 15 ~ 20 N·m to tighten the locking nut of the gear on the injection pump shaft, and lock it after adjusting the gap and aligning the marks.
Step 5: Loosen the injection pump shaft locking nut, insert the locking plate under the nut for positioning, and use a torque of (13 ± 2) N·m to lock the bolt; afterwards, pull out the process positioning pin, and then check whether the meshing clearance between the convex shaft timing gear and the injection pump gear is within the standard data range (0.08 ~ 0.33mm).
(2) Adjustment Points for VE Distributor Pump
① Maximum Fuel Delivery Adjustment: The magnitude of the fuel delivery of the VE injection pump is adjusted by controlling the effective stroke length of the plunger (commonly known as fuel cut-off metering). The fuel quantity adjustment lever can be fixed at the support point A on the pump body (Fig 1-50), and the speed control lever can rotate around the support point B on the fuel quantity adjustment lever. When it is necessary to adjust the fuel supply (such as the rated working condition fuel quantity), the locking nut can be loosened, and the fuel quantity adjustment screw can be turned out (to reduce fuel supply) or turned in (to increase fuel supply).
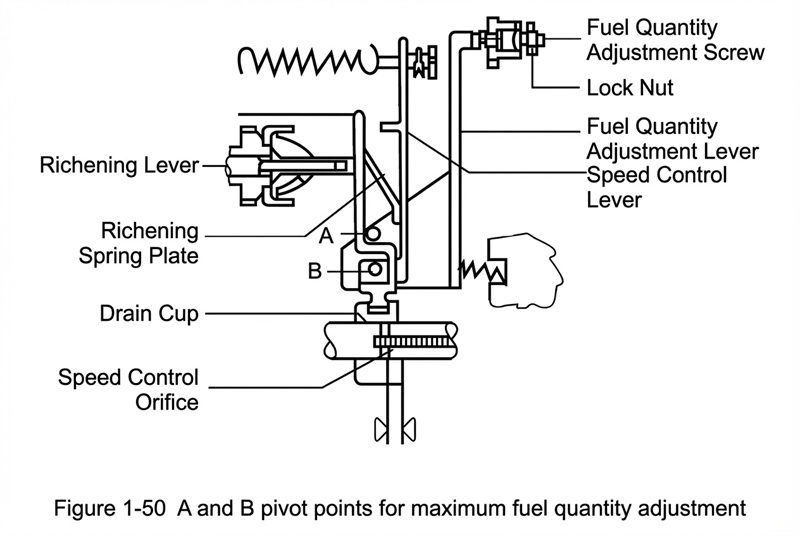
② Governor Adjustment: After the injection pump fuel supply adjustment is completed, the governor must be adjusted to obtain the rated speed at the rated fuel supply, the maximum limit (runaway/overspeed) speed, and the minimum stable (idle) speed.
a. High-speed Limit Screw Adjustment: Governor "Runaway" speed test. First, press the speed control arm to the bottom so that it contacts the high-speed limit screw; then check whether the fuel supply of the diesel engine at the rated speed meets the specified requirements of the diesel engine. Gradually increase the injection pump speed to reach the maximum limit (cut-off) speed. At this time, the single-cylinder fuel supply should be no more than 1mL/200 times. If the fuel supply is greater than the specified value, the high-speed limit screw can be turned out, which can reduce the fuel supply.
b. Idle Speed Screw Adjustment: Idle speed test. Fully release the speed control arm so that it contacts the idle speed adjustment screw, and run the injection pump at a speed of 250 ~ 300r/min (according to the idle speed requirements of the machine). Its single-cylinder fuel supply should comply with the diesel engine idle speed regulations. If the fuel supply is lower than the specified value during idling of the injection pump, the idle speed screw can be turned in until the adjustment is appropriate.
③ Injection Timing Adjustment: When the injection pump is at different speeds, the piston stroke of the injection timing mechanism should comply with the specified requirements. When checking the piston stroke, the cover plate with the spring on one end can be removed, and a special measuring tool can be installed to measure the piston stroke. When the piston stroke does not reach the specified value, the thickness of the shim can be correspondingly increased or decreased for adjustment (at least one shim must be installed at both ends of the spring). Then perform the injection timing adjustment. After installing the injection pump on the machine, the optimal fuel supply advance angle adjustment should be performed first. The specific steps are as follows:
a. First install the drive gear on the drive shaft of the injection pump; then fill the pump chamber with diesel fuel, exhaust the air, and connect the solenoid power supply; then slowly rotate the drive gear in the direction of normal operation.
b. Slowly rotate the diesel engine crankshaft to bring the first cylinder to the specified optimal fuel supply position.
c. Install the injection pump on the diesel engine so that the drive gear meshes with the corresponding drive gear on the diesel engine.
Note: Be strictly careful during the assembly process to prevent the transmission gear of the injection pump from rotating, so as to ensure the correct position where the injection pump starts to supply fuel.
d. Tighten the fastening nut on the injection pump flange.
e. Rotate the diesel engine crankshaft and carefully observe whether the advance angle when the first cylinder of the injection pump starts to discharge oil complies with the regulations. If the fuel supply advance angle has a deviation, it can be adjusted by rotating the injection pump housing (rotate the pump housing towards the pump rotation direction).
If the advance angle difference is large and cannot be reached by rotating the pump housing, the injection pump must be removed, and the meshing position of the drive gear and the pump drive shaft gear must be readjusted until the fuel supply advance angle complies with the regulations.
f. If the injection pump shaft was not locked during disassembly, causing the injection pump fuel supply timing to be disordered, the method for adjusting the injection pump fuel supply timing is:
-
Find the lowest point of the plunger: Install the special pre-stroke dial gauge into the center hole of the six outlets of the injection pump head, turn the semi-circular key on the injection pump shaft to the vicinity of the scribed line on the pump flange, and gently rotate the pump shaft back and forth. At this time, when the pointer of the dial gauge does not oscillate, it is the lowest point.
-
Adjustment of the plunger displacement: Adjust the dial gauge to the zero position, then slowly rotate the pump shaft clockwise. When the dial gauge needle reaches (2.35 ± 0.02) mm, lock the pump shaft, remove the pre-stroke dial gauge, and install the screw plug. At this time, the adjustment work of the injection pump fuel supply timing is completed.
④ Internal Pump Pressure Adjustment: Adjust the VE pump speed to 1500r/min. When the LDA device inlet pressure is 0.1MPa, the internal cavity pressure is 0.6 ~ 0.66MPa. If the value does not match, the pressure regulating valve spring of the VE pump fuel transfer pump can be adjusted, while checking whether the VE pump internal cavity pressure meets the corresponding requirements at other specified speeds.
⑤ Fuel Return Adjustment: Check whether the fuel return volume reaches the specified value at the specified speed. The fuel return volume and the pressure of the pressure regulating valve of the fuel transfer pump inside the VE pump affect each other, and the two should be checked repeatedly.
⑥ Start Oil Volume: Adjust the VE pump speed to 100r/min and check whether the fuel supply of the VE pump reaches the requirement.
⑦ Stop Device Function Check: Move the handle to the fuel cut-off direction at the specified speed; the fuel supply of the VE pump should be less than the specified value. Cut off the solenoid circuit at the specified speed; the fuel supply of the VE pump should be less than the specified value.
⑧ Pre-stroke Inspection and Adjustment: The specified value of the injection pump pre-stroke is (0 ± 0.02) mm. During detection, install a transparent spill tube on the screw hole of the plug at the upper end of the injection pump, slowly rotate the injection pump drive shaft to make the oil flow out of the spill tube, but not flow out from the spill tube. Then, remove the spill tube, replace it with a dial gauge to measure the position of the injection pump plunger at this time and read the value. Rotate the injection pump drive shaft so that the plunger is at the bottom dead center, i.e., the left limit position. Similarly, use the dial gauge to measure the plunger position at this time and record the reading. The difference between the two readings is the pre-stroke. If the pre-stroke does not meet the specified value, use a plunger adjustment shim to adjust. After replacing the plunger shim, it must be detected and adjusted according to the above methods and requirements.
⑨ Full Load Fuel Quantity Adjustment: Adjust the VE pump speed to 1900r/min. Under the condition that the inlet pressure of the LDA device is 0.1MPa, hold the control handle against the high-speed limit screw and check whether the fuel supply of the VE pump meets the requirements. Otherwise, use the maximum fuel supply adjustment screw to adjust; turning it out decreases the fuel amount; turning it in increases the fuel amount. At the same time, check whether the fuel supply deviation of each cylinder meets the requirements. In addition, the full load fuel quantity at other specified speeds needs to be checked. It needs to be explained that the fuel supply of the injection pump interacts with its internal cavity pressure. After adjusting the fuel supply of the injection pump, the internal cavity pressure must be rechecked to see if it exceeds the specified value.
⑩ Timer (Injection Advance) Automatic Adjuster Check and Adjustment: Remove the timer cover and install the adjuster detection device. Under the condition that the VE pump speed is adjusted to 1150r/min and the inlet air pressure is 0.1MPa, adjust the adjuster stroke to 1.6 ~ 2.0mm. If it does not conform to the specified value, adjust the thickness of the adjuster shim or replace the adjuster spring.
⑪ LDA Device Operating Point Adjustment: Hold the control handle tightly against the high-speed limit screw, adjust the VE pump speed to the specified value, import compressed air of different pressures into the LDA device, and check whether it starts to act under the specified compressed air pressure. If it does not act, the adjustment gear wheel should be turned to adjust.
⑫ High-speed Limit Screw Adjustment: Hold the control handle tightly against the high-speed limit screw and adjust the high-speed limit screw so that the starting speed is higher than the rated speed by 20 ~ 30r/min. At the same time, check whether the fuel cutoff speed meets the requirements.
⑬ Idle Speed Limit Screw Adjustment: Hold the control handle tightly against the idle speed limit screw, adjust the VE pump speed to idle, and adjust the idle limit screw so that the fuel supply of the oil pump reaches the specified idle fuel quantity. Check whether the fuel supply of each cylinder should be within the specified range. At the same time, check whether the idle stop conforms to the requirements.
⑭ Kf Dimension Adjustment: The adjustment of the Kf dimension is the adjustment of the pre-tension of the VE pump distributor plunger return spring. Install the guide pin, adjustment shim, return spring upper seat, etc., on the pump head of the distributor pump according to the relative positions when originally disassembled, then insert the plunger, return spring lower seat, etc., together. Insert the dial gauge into the special measuring head, screw the measuring head into the screw hole of the distributor pump equipped with the plunger, and measure the distance between the top surface of the plunger and the end face of the plunger sleeve. When the plunger return spring is not compressed, the measured distance mentioned above is the Kf dimension. The Kf dimension of the VE injection pump is 5.2 ~ 5.4mm. If the Kf dimension does not match, the thickness of the adjustment shim guiding the pin needs to be changed [Fig 1-51 (a), (b)].
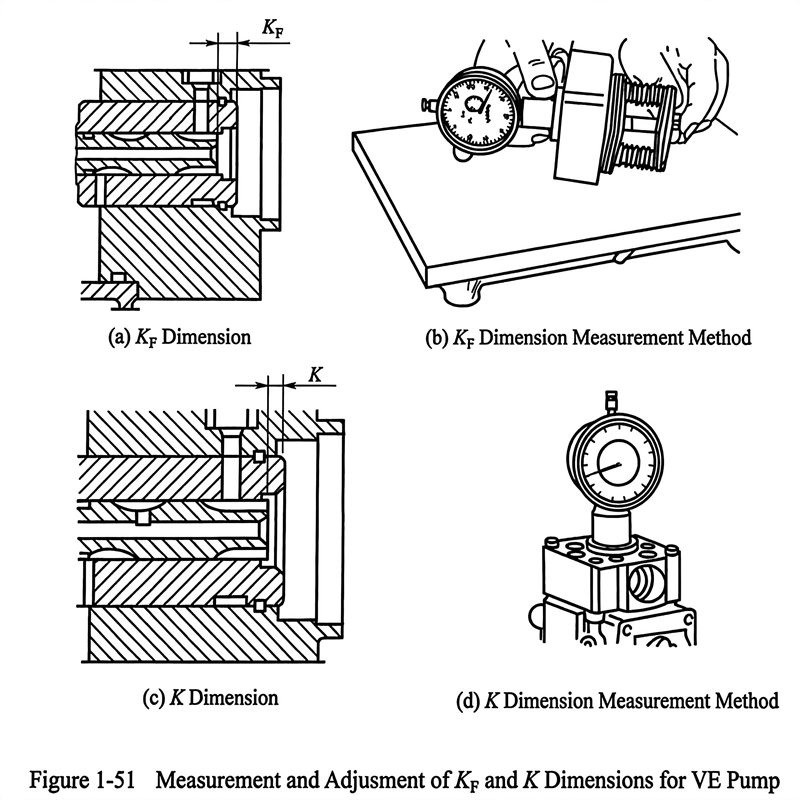
⑮ K Dimension Adjustment: After the Kf dimension is adjusted properly, install the guide pin, adjustment shim, return spring upper seat, plunger return spring, speed control lever assembly spring, O-ring seal, plunger, return spring lower seat, and oil volume control slider, etc., on the hydraulic head according to the original relative positions when disassembled, so that the notch on the plunger end engages with the drive shaft slot of the drive disc.
Fix the pump head on the pump body with a torque of 11 ~ 13N·m. Use the special measuring head and dial gauge to measure the distance between the top surface of the plunger and the end face of the plunger sleeve. This distance is the K dimension. The K dimension of the VE injection pump is 3.3mm. If the K dimension does not meet the requirements, the plunger adjustment shim can be selected for adjustment. The thickness of the plunger adjustment shim is 1.78 ~ 2.90mm, with one specification every 0.02mm, totaling 56 types available for selection [Fig 1-51 (c), (d)].
⑯ M5 Dimension Adjustment: Install the maximum fuel quantity adjustment screw and make the screw protrude to the measuring surface before disassembly of the governor cover. Fix the special tool on the pump body, and keep the adjustment lever in contact with a certain positioning pin of the special tool. Then use a thickness gauge to measure the gap between the slider and the lever. This gap is the Ms dimension. The Ms dimension of the VE pump is 0.8 ~ 1.0mm. If the Ms dimension does not match, the slider assembly on the governor assembly should be disassembled again, and a slider sleeve of suitable thickness should be replaced.
(3) Structure and Working Principle of Boost Compensator LDA
The exhaust gas turbocharger increases the intake air volume of the diesel engine. Therefore, compared with a naturally aspirated diesel engine, the size and speed of the diesel engine are almost unchanged, while the output power is greatly increased, and the effective efficiency will also increase due to the increase in air volume. In addition, it can also reduce fuel consumption. The supercharging of diesel engines is achieved through exhaust gas turbochargers.
As shown in Figure 1-52, the boost compensator consists of a diaphragm, a conical shaft, a diaphragm spring, a pusher rod, and a lever assembly on the upper part of the oil pump.
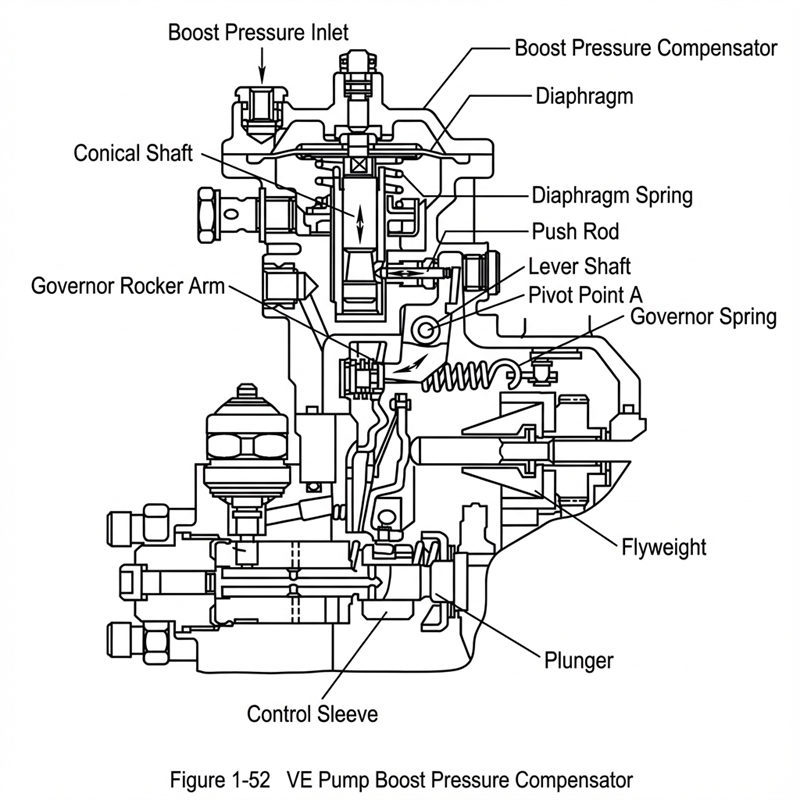
When the diesel engine speed decreases, the turbocharger's boosting efficiency decreases, the intake pressure decreases, and the pressure in the upper and lower air chambers decreases. Under the action of the diaphragm spring, the diaphragm and the conical shaft move upward. Due to the conical surface effect, the pusher rod moves to the right, and the lever rotates clockwise around the support point A and pushes the rocker arm of the governor to rotate counterclockwise, causing the control sleeve on the plunger to move to the right until the top of the conical shaft touches the adjustment screw on the top of the boost compensator. At this time, the boost compensator work ends, and the fuel volume is reduced to the minimum. This allows the diesel engine to maintain a suitable air-fuel ratio at low speeds to ensure complete combustion and avoid the phenomenon of black smoke at low speeds.
When the diesel engine speed increases, the intake pressure increases, and the pressure difference between the two air chambers becomes larger, causing the conical shaft to move downward. This causes the control sleeve to move to the left, and the fuel volume increases to meet the needs of the diesel engine.
The boost compensator body and the oil pump governor cover are integrated. The diaphragm divides the boost compensator into upper and lower parts. The upper air chamber of the diaphragm is connected to the intake pipe of the diesel engine, and the lower part of the diaphragm communicates with the atmosphere. Depending on the dynamic balance between the pressure difference of the upper and lower air chambers and the force of the diaphragm spring under the diaphragm, the position of the conical shaft connected to the diaphragm is determined, and the position of the governor rocker arm is changed through the pusher rod and lever to change the fuel supply.
The working range of the boost compensator fuel quantity correction is to change the lowest speed of the working range by adjusting the adjustment screw on the top of the boost compensator; by adjusting the gear ring, the preload of the spring can be changed, thereby changing the initial action time of the diaphragm. The pressure difference between the upper and lower pressure chambers changes accordingly. Through the reasonable adjustment of these two aspects, the fuel quantity correction speed range required by the turbocharged diesel engine can be obtained. The conical axis of the conical shaft and the axis of the guide part are eccentric. Changing the cone angle of the conical shaft and the installation position can obtain the fuel supply characteristics required by the diesel engine.
(4) Assembly Precautions for VE Distributor Pump
When the VE distributor pump is disassembled and reassembled, attention should be paid to the following points:
① When assembling, one must be serious and meticulous and observe the correct assembly sequence. When assembling, all O-ring seals and gaskets should be replaced.
② When installing the feed pump, put the eccentric ring into the drive shaft, use the drive shaft to pull the eccentric ring into the pump body, ensuring the eccentric ring hole faces the outlet hole, and the wide side faces the pump body front oil return hole side. When installing the sliding blades, note that the groove on the sliding blade should face inward. Ensure the two screws of the feed pump cover are tightened symmetrically, and the rotor and sliding blades should rotate flexibly and freely.
③ When installing the drive shaft, the side of the drive gear with a step should face the drive shaft fork direction, and install the shock absorber block; after installing the drive shaft shim and the drive shaft key, insert the feed pump hole; the drive shaft drive key must be installed into the keyway of the feed pump.
④ The side of the timer piston spring with a hole should face the timer return oil hole direction, and shims must be installed on both sides of the timer spring.
⑤ When installing the roller holder, the four rollers must be of equal height, the roller seat pin should be flexible and free, the movement between the roller holder and the pin should be flexible, and there should be no sticking phenomenon between the roller holder and the pin.
⑥ When installing the cam plate, the convex plate positioning pin and the drive shaft keyway should maintain the same direction.
⑦ When installing the governor bracket, slowly screw the governor support pin into the governor support point hole, and then tighten it.
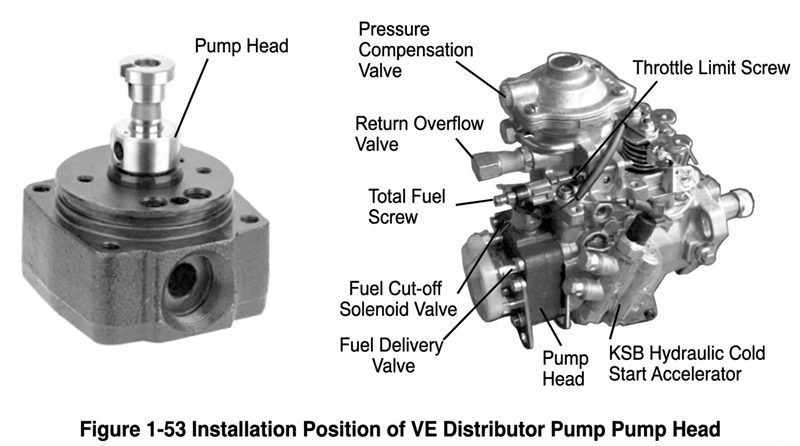
⑧ Pump Head Assembly: (The specific assembly of the VE distributor pump head and approximate installation position is shown in Figure 1-53). Key points are as follows:
a. Pay attention to measuring the Kf value and K value, making them reach the specified requirements.
Kf Value: The distance from the plunger head to the end face of the distribution sleeve when the pump head is in a free state, equipped with the spring upper and lower seats, spring guide rod, plunger spring, plunger shim, plunger shock absorption shim, and plunger spring shim. The size of the Kf value can be changed by the plunger spring shim.
K Value: The distance from the plunger core head to the end face of the distribution sleeve after the pump head is installed into the pump body. The size of the K value can be changed by the plunger adjustment shim.
b. New pump head screws should be used.
c. The gap between the speed control lever ball head and the pump head control radial hole must be flexible and free.
⑨ Flyweight Installation: Pay attention to the clearance between the flyweight holder and the gear, controlled at 0.10 ~ 0.35mm. If not within the range, adjust the governor shaft shim. The distance from the governor shaft end face to the pump body flange face should be 1.5 ~ 2.0mm.
⑩ Tightening Torque of VE Pump: The tightening torques of various main parts in the VE type distributor pump assembly are:
Pump head plug: 80 ~ 100 N·m.
Pump head screw: 11 ~ 13 N·m.
Delivery valve holder: 35 ~ 45 N·m.
Solenoid valve: 20 ~ 25 N·m.
Bracket screw: 10 ~ 13 N·m.
Pressure regulating valve: 8 ~ 9 N·m.
Related products


 Language
Language 

